Optimistic State
When building user experiences, the perception of performance is sometimes just as important as the actual performance of the code. In general, users don’t like waiting for an action to finish to see the result, and anything that takes more than a few milliseconds could be considered “slow” or “unresponsive” from the user’s perspective.
Developers can help mitigate this negative perception by presenting a successful UI state before the background task is fully completed. An example of this would be tapping a “Subscribe” button, and seeing it change to “Subscribed” instantly, even if the background call to the subscription API is still running.
This technique is known as Optimistic State, Optimistic UI or Optimistic User Experience. In this recipe, you will implement an application feature using Optimistic State and following the Flutter architecture guidelines.
Example feature: a subscribe button
#This example implements a subscribe button similar to the one you could find in a video streaming application or a newsletter.
When the button is tapped, the application then calls an external API, performing a subscription action, for example recording in a database that the user is now in the subscription list. For demo purposes, you will not implement the actual backend code, instead you will replace this call with a fake action that will simulate a network request.
In the case that the call is successful, the button text will change from “Subscribe” to “Subscribed”. The button background color will change as well.
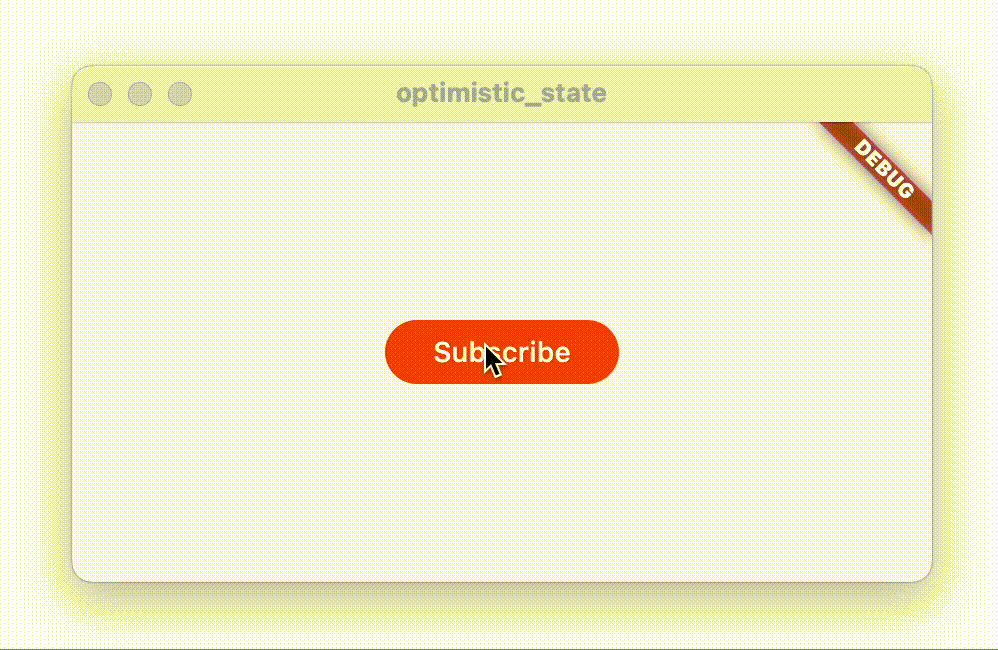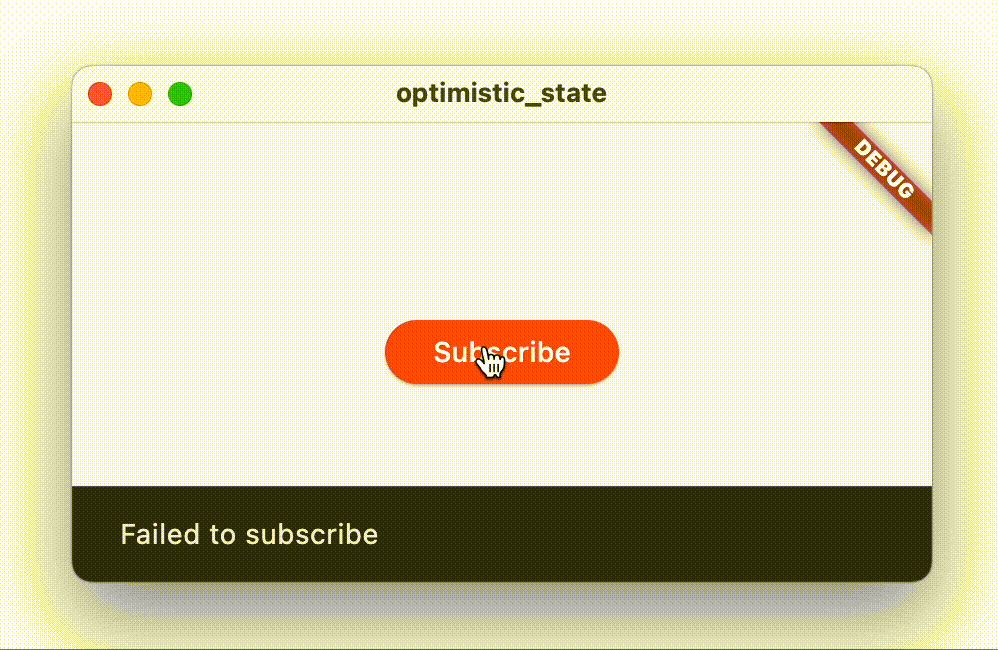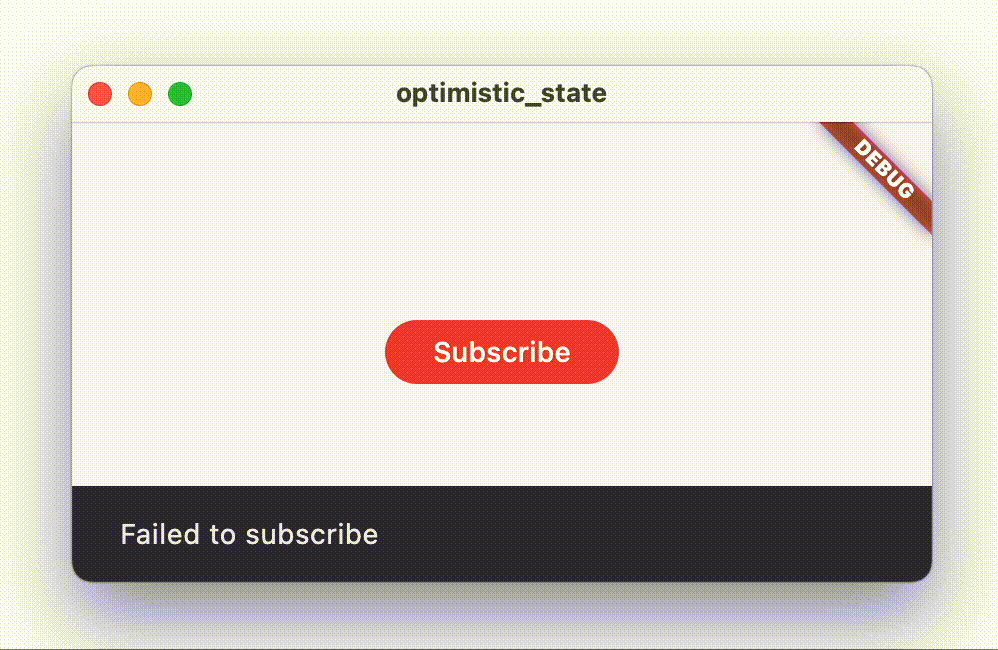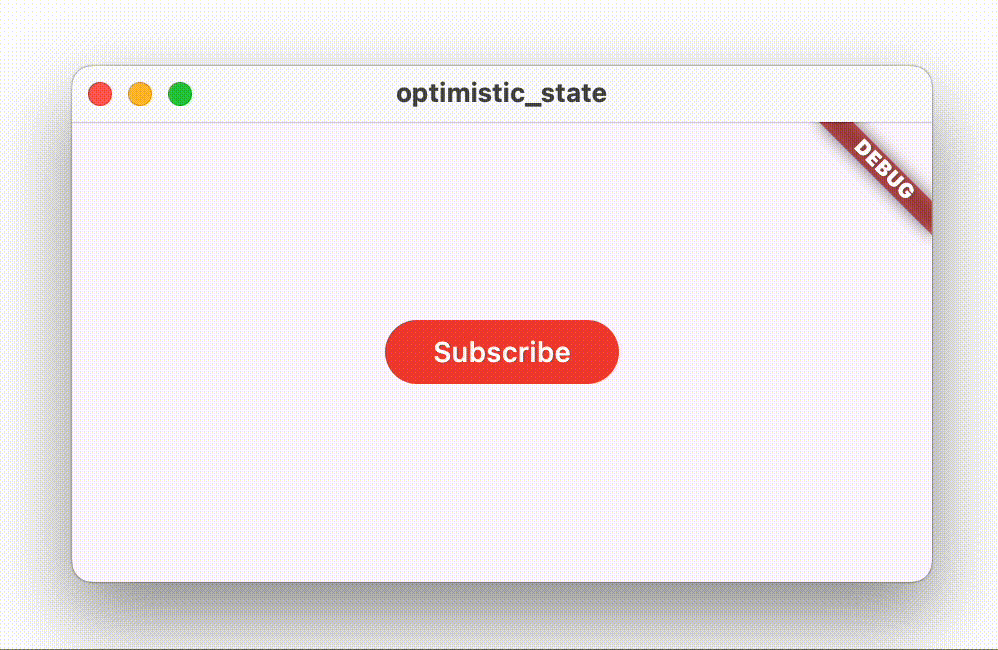
On the contrary, if the call fails, the button text should revert back to “Subscribe”, and the UI should show an error message to the user, for example using a Snackbar.
Following the Optimistic State idea, the button should instantly change to “Subscribed” once it is tapped, and only change back to “Subscribe” if the request failed.
Feature architecture
#Start by defining the feature architecture. Following the architecture guidelines, create these Dart classes in a Flutter project:
- A
StatefulWidgetnamedSubscribeButton - A class named
SubscribeButtonViewModelextendingChangeNotifier - A class named
SubscriptionRepository
class SubscribeButton extends StatefulWidget {
const SubscribeButton({
super.key,
});
@override
State<SubscribeButton> createState() => _SubscribeButtonState();
}
class _SubscribeButtonState extends State<SubscribeButton> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return const Placeholder();
}
}
class SubscribeButtonViewModel extends ChangeNotifier {}
class SubscriptionRepository {}The SubscribeButton widget and the SubscribeButtonViewModel represent the presentation layer of this solution. The widget is going to display a button that will show the text “Subscribe” or “Subscribed” depending on the subscription state. The view model will contain the subscription state. When the button is tapped, the widget will call the view model to perform the action.
The SubscriptionRepository will implement a subscribe method that will throw an exception when the action fails. The view model will call this method when performing the subscription action.
Next, connect them together by adding the SubscriptionRepository to the SubscribeButtonViewModel:
class SubscribeButtonViewModel extends ChangeNotifier {
SubscribeButtonViewModel({
required this.subscriptionRepository,
});
final SubscriptionRepository subscriptionRepository;
}And add the SubscribeButtonViewModel to the SubscribeButton widget:
class SubscribeButton extends StatefulWidget {
const SubscribeButton({
super.key,
required this.viewModel,
});
/// Subscribe button view model.
final SubscribeButtonViewModel viewModel;
@override
State<SubscribeButton> createState() => _SubscribeButtonState();
}Now that you have created the basic solution architecture, you can create the SubscribeButton widget the following way:
SubscribeButton(
viewModel: SubscribeButtonViewModel(
subscriptionRepository: SubscriptionRepository(),
),
)Implement the SubscriptionRepository
#Add a new asynchronous method named subscribe() to the SubscriptionRepository with the following code:
class SubscriptionRepository {
/// Simulates a network request and then fails.
Future<void> subscribe() async {
// Simulate a network request
await Future.delayed(const Duration(seconds: 1));
// Fail after one second
throw Exception('Failed to subscribe');
}
}The call to await Future.delayed() with a duration of one second has been added to simulate a long running request. The method execution will pause for a second, and then it will continue running.
In order to simulate a request failing, the subscribe method throws an exception at the end. This will be used later on to show how to recover from a failed request when implementing Optimistic State.
Implement the SubscribeButtonViewModel
#To represented the subscription state, as well a possible error state, add the following public members to the SubscribeButtonViewModel:
// Whether the user is subscribed
bool subscribed = false;
// Whether the subscription action has failed
bool error = false;Both are set to false on start.
Following the ideas of Optimistic State, the subscribed state will change to true as soon as the user taps the subscribe button. And will only change back to false if the action fails.
The error state will change to true when the action fails, indicating the SubscribeButton widget to show an error message to the user. The variable should go back to false once the error has been displayed.
Next, implement an asynchronous subscribe() method:
// Subscription action
Future<void> subscribe() async {
// Ignore taps when subscribed
if (subscribed) {
return;
}
// Optimistic state.
// It will be reverted if the subscription fails.
subscribed = true;
// Notify listeners to update the UI
notifyListeners();
try {
await subscriptionRepository.subscribe();
} catch (e) {
print('Failed to subscribe: $e');
// Revert to the previous state
subscribed = false;
// Set the error state
error = true;
} finally {
notifyListeners();
}
}As described previously, first the method sets the subscribed state to true and then calls to notifyListeners(). This forces the UI to update and the button changes its appearance, showing the text “Subscribed” to the user.
Then the method performs the actual call to the repository. This call is wrapped by a try-catch in order to catch any exceptions it may throw. In case an exception is caught, the subscribed state is set back to false, and the error state is set to true. A final call to notifyListeners() is done to change the UI back to ‘Subscribe’.
If there is no exception, the process is complete because the UI is already reflecting the success state.
The complete SubscribeButtonViewModel should look like this:
/// Subscribe button View Model.
/// Handles the subscribe action and exposes the state to the subscription.
class SubscribeButtonViewModel extends ChangeNotifier {
SubscribeButtonViewModel({
required this.subscriptionRepository,
});
final SubscriptionRepository subscriptionRepository;
// Whether the user is subscribed
bool subscribed = false;
// Whether the subscription action has failed
bool error = false;
// Subscription action
Future<void> subscribe() async {
// Ignore taps when subscribed
if (subscribed) {
return;
}
// Optimistic state.
// It will be reverted if the subscription fails.
subscribed = true;
// Notify listeners to update the UI
notifyListeners();
try {
await subscriptionRepository.subscribe();
} catch (e) {
print('Failed to subscribe: $e');
// Revert to the previous state
subscribed = false;
// Set the error state
error = true;
} finally {
notifyListeners();
}
}
}Implement the SubscribeButton
#In this step, you will first implement the build method of the SubscribeButton, and then implement the feature’s error handling.
Add the following code to the build method:
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return ListenableBuilder(
listenable: widget.viewModel,
builder: (context, _) {
return FilledButton(
onPressed: widget.viewModel.subscribe,
style: widget.viewModel.subscribed
? SubscribeButtonStyle.subscribed
: SubscribeButtonStyle.unsubscribed,
child: widget.viewModel.subscribed
? const Text('Subscribed')
: const Text('Subscribe'),
);
},
);
}This build method contains a ListenableBuilder that listens to changes from the view model. The builder then creates a FilledButton that will display the text "Subscribed" or "Subscribe" depending on the view model state. The button style will also change depending on this state. As well, when the button is tapped, it runs the subscribe() method from the view model.
The SubscribeButtonStyle can be found here. Add this class next to the SubscribeButton. Feel free to modify the ButtonStyle.
class SubscribeButtonStyle {
static const unsubscribed = ButtonStyle(
backgroundColor: WidgetStatePropertyAll(Colors.red),
);
static const subscribed = ButtonStyle(
backgroundColor: WidgetStatePropertyAll(Colors.green),
);
}If you run the application now, you will see how the button changes when you press it, however it will change back to the original state without showing an error.
Handling errors
#To handle errors, add the initState() and dispose() methods to the SubscribeButtonState, and then add the _onViewModelChange() method.
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
widget.viewModel.addListener(_onViewModelChange);
}
@override
void dispose() {
widget.viewModel.removeListener(_onViewModelChange);
super.dispose();
}/// Listen to ViewModel changes.
void _onViewModelChange() {
// If the subscription action has failed
if (widget.viewModel.error) {
// Reset the error state
widget.viewModel.error = false;
// Show an error message
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
const SnackBar(
content: Text('Failed to subscribe'),
),
);
}
}The addListener() call registers the _onViewModelChange() method to be called when the view model notifies listeners. It’s important to call removeListener() when the widget is disposed of, in order to avoid errors.
The _onViewModelChange() method checks the error state, and if it is true, displays a Snackbar to the user showing an error message. As well, the error state is set back to false, to avoid displaying the error message multiple times if notifyListeners() is called again in the view model.
Advanced Optimistic State
#In this tutorial, you’ve learned how to implement an Optimistic State with a single binary state, but you can use this technique to create a more advanced solution by incorporating a third temporal state that indicates that the action is still running.
For example, in a chat application when the user sends a new message, the application will display the new chat message in the chat window, but with an icon indicating that the message is still pending to be delivered. When the message is delivered, that icon would be removed.
In the subscribe button example, you could add another flag in the view model indicating that the subscribe() method is still running, or use the Command pattern running state, then modify the button style slightly to show that the operation is running.
Interactive example
#This example shows the SubscribeButton widget together with the SubscribeButtonViewModel and SubscriptionRepository, which implement a subscribe tap action with Optimistic State.
When you tap the button, the button text changes from “Subscribe” to “Subscribed”. After a second, the repository throws an exception, which gets captured by the view model, and the button reverts back to showing “Subscribe”, while also displaying a Snackbar with an error message.
// ignore_for_file: avoid_print
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: SubscribeButton(
viewModel: SubscribeButtonViewModel(
subscriptionRepository: SubscriptionRepository(),
),
),
),
),
);
}
}
/// A button that simulates a subscription action.
/// For example, subscribing to a newsletter or a streaming channel.
class SubscribeButton extends StatefulWidget {
const SubscribeButton({
super.key,
required this.viewModel,
});
/// Subscribe button view model.
final SubscribeButtonViewModel viewModel;
@override
State<SubscribeButton> createState() => _SubscribeButtonState();
}
class _SubscribeButtonState extends State<SubscribeButton> {
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
widget.viewModel.addListener(_onViewModelChange);
}
@override
void dispose() {
widget.viewModel.removeListener(_onViewModelChange);
super.dispose();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return ListenableBuilder(
listenable: widget.viewModel,
builder: (context, _) {
return FilledButton(
onPressed: widget.viewModel.subscribe,
style: widget.viewModel.subscribed
? SubscribeButtonStyle.subscribed
: SubscribeButtonStyle.unsubscribed,
child: widget.viewModel.subscribed
? const Text('Subscribed')
: const Text('Subscribe'),
);
},
);
}
/// Listen to ViewModel changes.
void _onViewModelChange() {
// If the subscription action has failed
if (widget.viewModel.error) {
// Reset the error state
widget.viewModel.error = false;
// Show an error message
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
const SnackBar(
content: Text('Failed to subscribe'),
),
);
}
}
}
class SubscribeButtonStyle {
static const unsubscribed = ButtonStyle(
backgroundColor: WidgetStatePropertyAll(Colors.red),
);
static const subscribed = ButtonStyle(
backgroundColor: WidgetStatePropertyAll(Colors.green),
);
}
/// Subscribe button View Model.
/// Handles the subscribe action and exposes the state to the subscription.
class SubscribeButtonViewModel extends ChangeNotifier {
SubscribeButtonViewModel({
required this.subscriptionRepository,
});
final SubscriptionRepository subscriptionRepository;
// Whether the user is subscribed
bool subscribed = false;
// Whether the subscription action has failed
bool error = false;
// Subscription action
Future<void> subscribe() async {
// Ignore taps when subscribed
if (subscribed) {
return;
}
// Optimistic state.
// It will be reverted if the subscription fails.
subscribed = true;
// Notify listeners to update the UI
notifyListeners();
try {
await subscriptionRepository.subscribe();
} catch (e) {
print('Failed to subscribe: $e');
// Revert to the previous state
subscribed = false;
// Set the error state
error = true;
} finally {
notifyListeners();
}
}
}
/// Repository of subscriptions.
class SubscriptionRepository {
/// Simulates a network request and then fails.
Future<void> subscribe() async {
// Simulate a network request
await Future.delayed(const Duration(seconds: 1));
// Fail after one second
throw Exception('Failed to subscribe');
}
}
Unless stated otherwise, the documentation on this site reflects the latest stable version of Flutter. Page last updated on 2024-11-21. View source or report an issue.