Add a Flutter View to an Android app
Learn how to perform advanced integrations via Flutter Views.
Integrating via a FlutterView requires a bit more work than via FlutterActivity and FlutterFragment previously described.
Fundamentally, the Flutter framework on the Dart side requires access to various activity-level events and lifecycles to function. Since the FlutterView (which is an android.view.View) can be added to any activity which is owned by the developer's application and since the FlutterView doesn't have access to activity level events, the developer must bridge those connections manually to the FlutterEngine.
How you choose to feed your application's activities' events to the FlutterView will be specific to your application.
A sample
#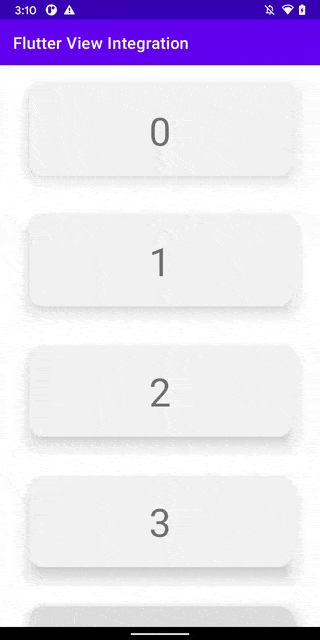
Unlike the guides for FlutterActivity and FlutterFragment, the FlutterView integration could be better demonstrated with a sample project.
A sample project is at https://github.com/flutter/samples/tree/main/add_to_app/android_view to document a simple FlutterView integration where FlutterViews are used for some of the cells in a RecycleView list of cards as seen in the gif above.
General approach
#
The general gist of the FlutterView-level integration is that you
must recreate the various interactions between your Activity, the
FlutterView
and the
FlutterEngine
present in the FlutterActivityAndFragmentDelegate
in your own application's code.
The connections made in the
FlutterActivityAndFragmentDelegate
are done automatically when using a
FlutterActivity
or a
FlutterFragment,
but since the FlutterView
in this case is being added to an Activity or Fragment in your application,
you must recreate the connections manually.
Otherwise, the FlutterView
won't render anything or have other missing functionalities.
A sample
FlutterViewEngine
class shows one such possible implementation of an application-specific
connection between an Activity, a
FlutterView
and a FlutterEngine.
APIs to implement
#The absolute minimum implementation needed for Flutter to draw anything at all is to:
-
Call
attachToFlutterEnginewhen theFlutterViewis added to a resumedActivity's view hierarchy and is visible; and -
Call
appIsResumedon theFlutterEngine'slifecycleChannelfield when theActivityhosting theFlutterViewis visible.
The reverse
detachFromFlutterEngine
and other lifecycle methods on the
LifecycleChannel
class must also be called to not leak resources when the
FlutterView or Activity is no longer visible.
In addition, see the remaining implementation in the
FlutterViewEngine
demo class or in the
FlutterActivityAndFragmentDelegate
to ensure a correct functioning of other features such as clipboards,
system UI overlay, plugins, and so on.
Content-sized views
#
Usually, a FlutterView
needs fixed dimensions either through it's own dimensions or by matching a
parent's dimensions. This can be seen in the sample project.
However, it's now possible to allow FlutterView to size itself
based on its content. By using, content_wrap for either the height
or the width a FlutterView can size itself, as shown in the content sized sample project.
-
To enable Content-sized view when deploying your app,
add the following setting to your project's
AndroidManifest.xmlfile under the<application>tag:
<meta-data
android:name="io.flutter.embedding.android.EnableContentSizing"
android:value="true" />
Restrictions
#Since content-sized Flutter views require your Flutter app to be able to size itself, some widgets are not supported.
- A widget with unbounded size, like a
ListView. - A widget that defers to its child for the size, like
LayoutBuilder.
In practice, this means that quite a few common widgets are not supported,
such as ScaffoldBuilder, CupertinoTimerPicker,
or any widget that internally relies on a LayoutBuilder.
When in doubt, you can use an UnconstrainedBox to test the usability of
a widget for a content-sized view, as shown in the following example:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context)
=> MaterialApp(home: MyPage());
}
class MyPage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: UnconstrainedBox(
// TODO: Edit this line to check if a widget
// can cause problems with content-sized views.
child: Text('This works!'),
// child: Column(children: [Column(children: [Expanded(child: Text('This blows up!'))])]),
// child: ListView(children: [Text('This blows up!')]),
)
);
}
}
Unless stated otherwise, the documentation on this site reflects Flutter 3.41.2. Page last updated on 2026-02-03. View source or report an issue.